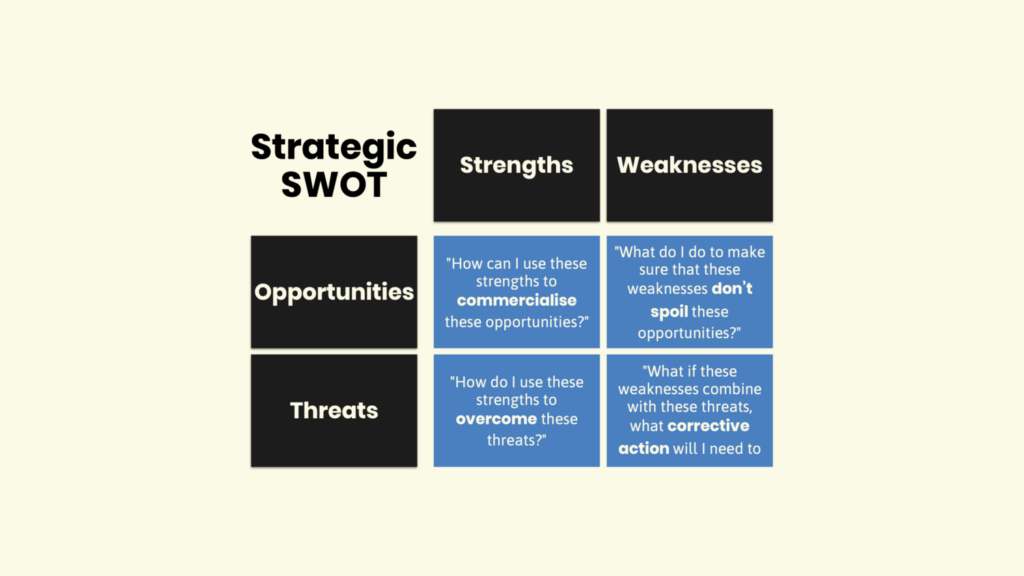
In leadership assessment, one strategic methodology has emerged as an invaluable tool: the SWOT analysis of a leader. This structured approach entails the exploration of a leader’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to gain a comprehensive understanding of their capabilities and potential areas for growth.
By delving into the intricacies of a leader’s attributes and the external forces that shape their effectiveness, a SWOT analysis of a leader offers a holistic view that aids in strategic decision-making and leadership development.
The acronym ‘SWOT’ stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats – key dimensions that collectively shape a leader’s performance and impact. Strengths encompass the leader’s inherent qualities and skills that empower them to guide teams, make critical decisions, and inspire change.
Conversely, weaknesses highlight areas where the leader may face challenges or require further development. While strengths propel leaders forward, defects present opportunities for growth and enhancement.
Understanding and analyzing these four parts of a SWOT analysis provides leaders with a comprehensive view of their professional landscape, aiding in strategic decision-making and personal development.
Moreover, the analysis extends beyond the leader’s internal attributes, incorporating the assessment of external factors that can influence their trajectory. Opportunities arise from the environment, such as emerging trends and pathways for professional growth, while threats encompass external challenges that might hinder the leader’s effectiveness.
This comprehensive evaluation equips organizations and individuals with actionable insights to optimize leadership strategies and ensure sustainable success.
Steps for Conducting a SWOT Analysis of a Leader
Identifying Strengths
The first step involves thoroughly identifying the leader’s strengths, encapsulating their positive attributes and distinctive qualities. These strengths could manifest in exceptional communication skills, visionary thinking, adept decision-making abilities, and the ability to inspire and motivate teams effectively.
By recognizing these strengths, a leader can further leverage them to drive organizational success and build market strategies.
Explore the leader’s past achievements, personal attributes, and feedback from peers and subordinates. These insights can provide a deeper understanding of how the leader’s strengths contribute to their effectiveness.
Strengths are the inherent qualities and attributes that make a leader effective and impactful. These are the characteristics that set them apart and enable them to lead with confidence.
To identify strengths:
- Gather Feedback: Solicit feedback from peers, subordinates, and superiors. Collect specific examples of when the leader excelled.
- Analyze Achievements: Review the leader’s track record of accomplishments and successful initiatives.
- Personality Traits: Identify personality traits that contribute to leadership, such as solid communication, empathy, and resilience.
- Adaptability: Recognize the leader’s ability to adapt to changing circumstances and navigate challenges.
Example: Consider a leader who consistently fosters an inclusive work environment. Their open communication style and active listening skills create a sense of belonging among team members.
Recognizing Weaknesses
This stage entails a focused effort on identifying the leader’s weaknesses – aspects that could hinder their performance or impact their overall effectiveness. These weaknesses might encompass challenges in delegating tasks, a tendency towards micromanagement, or limited adaptability to rapid changes in the business landscape.
To identify weaknesses, observe instances where the leader’s performance may have faltered or where they might have faced difficulties. Additionally, analyze feedback from peers and subordinates, as their insights can shed light on areas that need improvement.
Weaknesses are areas that may hinder a leader’s performance or effectiveness. Identifying and addressing these weaknesses is crucial for personal and professional growth.
To recognize weaknesses:
- Self-Reflection: Encourage the leader to reflect on their challenges and areas they wish to improve.
- 360-Degree Evaluation: Seek input from various sources to gain a well-rounded perspective on areas that need development.
- Skill Gaps: Identify specific skills or knowledge gaps that might impact leadership effectiveness.
- Feedback Channels: Establish an environment where receiving constructive feedback is encouraged.
Example: A leader might need help delegating tasks, leading to burnout and inefficiency. You can address this weakness through delegation workshops and coaching.
See also: 12 Best B2B Marketing Campaigns: Boost Your Business Growth
Exploring Opportunities
Opportunities are external factors that a leader can harness to enhance their leadership trajectory. This phase involves identifying emerging trends in their industry, the potential to lead cross-functional teams, or avenues for professional development that could further refine their leadership skills.
Look beyond the current scope of the leader’s role and examine trends in the industry and market. Consider how the leader can capitalize on these trends to bring innovation and growth to the organization.
Opportunities refer to external factors that leaders can leverage to enhance their leadership journey. Identifying and capitalizing on these opportunities can accelerate growth.
To explore opportunities:
- Industry Trends: Keep yourself updated with industry trends and technological advancements impacting leadership strategies.
- Networking: Encourage the leader to build a solid professional network, opening doors to collaborations and mentorship.
- Cross-Functional Exposure: Assign the leader to cross-functional projects that broaden their skill set and perspective.
- Learning and Development: Provide access to workshops, courses, and conferences that align with leadership goals.
Example: A leader in the technology sector might leverage the opportunity to enhance their understanding of emerging technologies, positioning them as an innovative leader in their organization.
Analyzing Threats
Threats are external factors that could undermine a leader’s effectiveness. This stage involves recognizing market disruptions, economic uncertainties, or shifts in organizational dynamics that require the leader to adapt their approach.
Analyze the competitive landscape, potential challenges posed by external factors, and organizational structure or goals changes. By identifying threats, leaders can proactively develop strategies to mitigate their impact.
Threats are external challenges that can affect a leader’s effectiveness. Awareness of these threats allows leaders to strategize and mitigate potential issues proactively.
To analyze threats:
- Market Dynamics: Monitor market shifts, competitors’ actions, and customer preferences that could impact the leader’s role.
- Economic Factors: Consider economic fluctuations and their potential effects on the leader’s decision-making.
- Organizational Changes: Anticipate organizational structure, culture, or strategy changes that might impact leadership dynamics.
- External Influences: Identify geopolitical or regulatory changes affecting the industry or organization.
Example: A leader in the retail sector might face the threat of increased competition from e-commerce giants. This threat can be addressed by developing strategies to enhance the in-store experience and customer loyalty.
By following these steps and conducting a thorough SWOT analysis of a leader, organizations can understand leadership dynamics deeply, identify growth areas, and implement strategic improvements that drive sustained success.
Read also: How to do Competitor SWOT Analysis? 101 Guide
Synthesizing the SWOT Analysis of a Leader
After gathering insights from the previous steps, it’s crucial to synthesize the information. This involves understanding how to utilize strengths to capitalize on opportunities, mitigate weaknesses to address threats, and how the overall analysis shapes the leader’s strategic direction.
Analyze the intersections between strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to formulate a comprehensive strategy. Consider how strengths can offset liabilities and how options can align with forces to drive growth.
FAQs (SWOT Analysis of a Leader)
How can I identify a leader's strengths?
Look for consistent patterns of behavior, notable accomplishments, and skills that set the leader apart. Seek input from team members and colleagues to gain a well-rounded perspective.
How can I address a leader's weaknesses?
Developing a plan for skill enhancement, providing relevant training, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement can help leaders overcome their weaknesses and grow professionally.
How do I identify opportunities for a leader's growth?
Stay informed about industry developments, network with peers, and actively encourage leaders to seek learning and development opportunities.
How can leaders prepare for potential threats?
Leaders should foster flexibility and agility in their approach, develop contingency plans, and encourage open communication to address potential threats swiftly.
Conclusion
A SWOT analysis of a leader serves as a valuable exercise to gain a holistic perspective on their leadership style and potential areas for improvement. People can also use other alternatives to SWOT Analysis to assess their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, and stakeholders can collaboratively work towards enhancing leadership effectiveness and steering the leader’s growth journey.
In conclusion, conducting a SWOT analysis of a leader involves comprehensively exploring the leader’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
This strategic evaluation offers a nuanced understanding of the leader’s capabilities, thus aiding their continuous development and growth as influential leaders in their respective domains.