SWOT analysis stands for ‘Strength, Weakness, Opportunity, and Threat.’ Additionally, it is a technique for evaluating a business. Furthermore, it helps identify what works for the business/company and tackle possible problems. Consequently, a company can explore potential strategies and keep on improving.
First, SWOT analysis helps a company identify its position compared to rivals. In addition, the four parts of SWOT analysis are generally rated using accurate market data. Furthermore, this method considers all the external and internal factors affecting the company.
In conclusion, an established and growing business needs to consider SWOT analysis. Therefore, a company needs to adapt to the market, and SWOT analysis is an effective method. Lastly, continue reading if you want to know how to do a SWOT analysis for your business.
SWOT Analysis: What are the Four Parts of a SWOT Analysis?
The answer to: What are the four parts of a SWOT analysis? Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It is essential to look at the SWOT analysis step-by-step.
The four parts of a SWOT analysis are as follows: –
Strengths: The Building Blocks of Success
It is essential to identify the strengths of the company. Muscles help a company to plan its strategies. Strengths are internal characteristics, sources, and resources given to the organization. Strengths are generally divided into two parts:
Tangible Strengths
These are things that can be classified into quantifiables and observables. For example:
- Financial Resources
- The capital, cash, and stock holdings count as financial resources.
- Physical Assets
- Resources such as factories, machines, and land come under physical assets.
- Human Resources
- The workforce/labor comes under human resources.
Intangible Strengths
These things are not subjective and cannot be measured with money precisely. For example:
- Brand Recognition
- Brand Recognition refers to the reputation of the company among the customers.
- Workforce Motivation
- Workforce loyalty refers to the workers’ morale and motivation to work.
Case Study: Ralph Lauren
Strengths:
Popular Brand
Ralph Lauren has built a strong brand image of luxury and is famous for its high-end polo products.
Variety of Products
They offer products beyond clothes, like furniture, perfume, and restaurants. This gives the customers many choices. This keeps the customers interested in the brand.
Opening Global Chains
Ralph Lauren has stores worldwide, which makes it accessible to many people.
Quality Control
They control many aspects of production and distribution, which ensures good quality.
Weaknesses: Identifying and Overcoming Internal Hurdles
The ‘W’ in SWOT analysis stands for weakness. Weakness here means the company’s internal faults and problems. Weaknesses can often ruin opportunities and make the company vulnerable to threats.
Types of Weaknesses:
Internal Weaknesses
- Internal weaknesses are the faults and problems that lie inside the organization.
Controllable Weakness:
- Weaknesses that can be controlled or worked upon by the company are known as controllable weaknesses.
Performance Inhibitors:
- They affect the efficiency of a company and, eventually, the financial revenue. These weaknesses jeopardize the company even after forming a proper strategy.
Examples of Weaknesses:
Outdated Technology
A company that uses outdated and old technology generally suffers. The new generation of customers wants new technology. The obsolete technology is often inefficient and complex to use.
Inadequate assets
A company needs more financial and labor assets to maintain its operations.
Poor communication
Internal miscommunication by the company or the managers leads to confusion. This results in missed opportunities.
Importance of Recognizing Weaknesses
Being able to recognize and address weaknesses can help the company. Examples:
Vulnerability to competition
- Unrecognized weaknesses can prevent the company from losing to its rivals. Not adapting and improving the product or the service can lead to unhappy customers.
Missed opportunities
- Failing to use advantages and the market conditions due to weaknesses are missed opportunities. Not using options wisely can lead to a decrease in a company’s growth.
Case Study: Weaknesses of Honda
Depending on the North American Region
Businesses explore ways to extend their operations globally so they don’t need to rely on one region for deals.
When we notice the incomes Honda earned from diverse districts, we can see that Honda mostly depends on one region. That is the North American region for its revenue. This acts as a weakness of the brand since any damage happening to the brand in North America can affect the whole company.
High Cost Products
Businesses, for the most part, attempt to keep the costs of their items low so that more individuals can buy them. As a result, clients are consequently drawn toward low-priced items.
However, Honda is one of the brands that offer costly items compared to its competitors. One of the reasons why Honda automobiles are expensive is that it has to manufacture plants overseas in countries like the US and Japan. The manufacturing costs of these countries have increased. As a result, the price of Honda items is additionally high.
Opportunities: Seizing External Chances for Growth
The ‘O’ in SWOT stands for opportunity. Opportunities are the potential strategies and methods to increase the brand’s growth.
Organizations can use new markets to their advantage as opportunities. They can use the latest technology to increase efficiency and produce superior products. Opportunities like marketing on social media platforms like Google, YouTube, etc, can also help companies.
Case Study
Opportunities of Samsung
Samsung introduced a large variety of innovative phones. For example, Samsung kept innovating, from sliding phones to flip phones and launching the Galaxy watch. This shows that Samsung sees new designs as an opportunity.
Opportunities of PepsiCo
PepsiCo saw that healthy products and substitutes were trending in the market. So, they used this opportunity to launch healthy food and beverages. They found a meat-free food company called Bare Snacks.
Threats: Navigating External Risks and Challenges
The ‘T’ in SWOT refers to threats. Threats are external factors that have the potential to have adverse effects on the company. It is essential to identify and manage threats as they can potentially decrease the revenue and profits of the company.
Threats can be known by the following:
- Studying Competitors
- Keeping up-to-date with new technologies
- Studying the market
- Managing and predicting environmental threats
Case Study:
Microsoft’s response to WannaCry ransomware
The WannaCry ransomware risked the image and trust of Microsoft among the users. But, Microsoft took the proper steps to manage the threats.
Microsoft took responsibility for the lack of security and started working on the solution. The company immediately released a security patch for the ransomware. They took customer care seriously and handled all the complaints. They provided necessary technical support and made the public aware of the solution.
These were the four steps of SWOT analysis.
Best Buy’s SWOT analysis also highlights growth opportunities, such as expanding into new markets or enhancing its online presence.
Step-by-Step Guide for SWOT Analysis
Many factors need to be looked at for doing a detailed SWOT analysis. You can look at the steps mentioned below for reference.
Step 1: Identify the Objective
A SWOT investigation can get very detailed. This is even though more value will likely be produced if the examination is pointed straightforwardly at an objective.
For illustration, the objective of a SWOT investigation may be centered, as it were, on whether to perform an unused item rollout. With an objective intellect, a company will have direction on what they trust to attain after the method. In this case, the SWOT investigation should assist in deciding whether or not the item should be introduced. You can also study the SWOT analysis of a market leader.
Step 2: Managing Resources
You should gather accurate market and company data for a practical SWOT analysis. Identify the limitations and the inaccurate data. Take the staff feedback and the feedback of all the resources for a detailed analysis. Taking into account all the factors like manufacturing and sales.
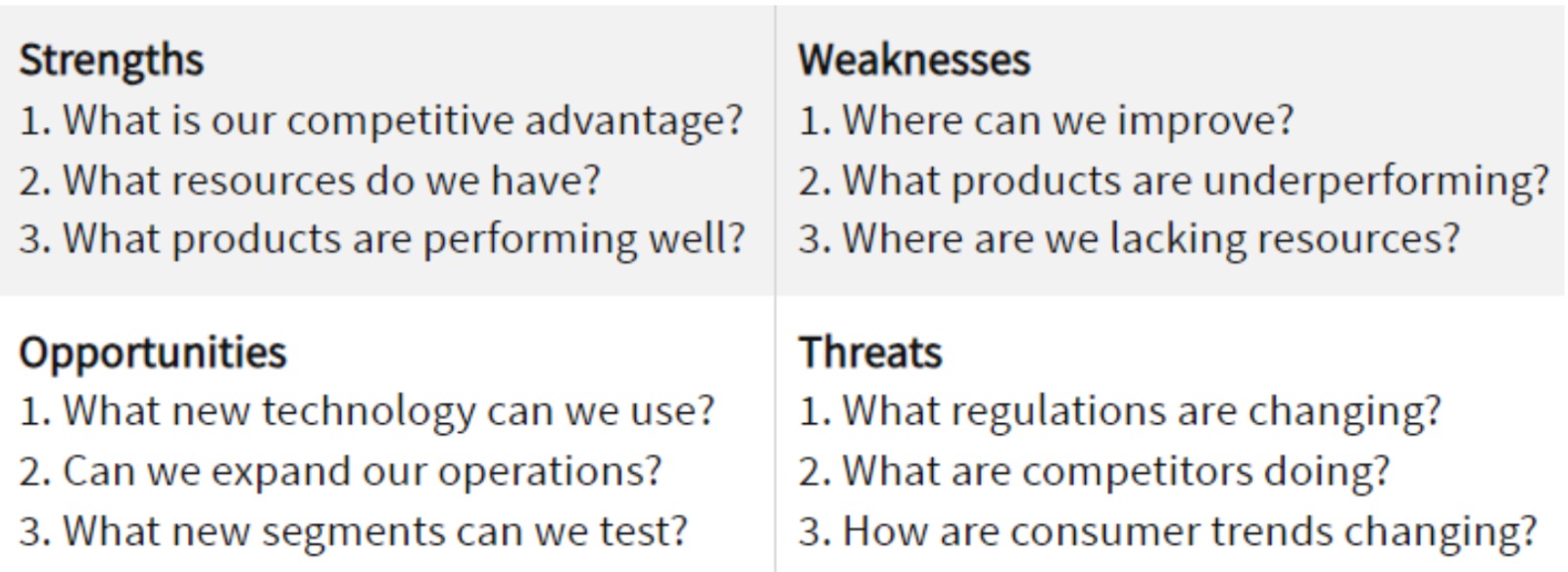
Step 3: Ask Relevant Questions
For a proper SWOT analysis, you must recognize strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. You must consider a specific set of questions and make a SWOT table. One such set of questions is:
Step 4: Analyzing Results
After forming a SWOT table, analyze the data and consider its applications. Additionally, convey the results to the appropriate authorities, who can take action. Then, work on strengths, decrease weaknesses, use opportunities, and eliminate threats.
You can also look at some famous SWOT analyses for reference. For example, the SWOT analysis of Twitter/X is an appropriate reference.
See Also: SWOT Analysis For a Clothing Business: Should You Start It?
Benefits of SWOT Analysis
- Identifying problems and finding appropriate solutions.
- This analysis can be applied to every business and company.
- This analysis provides both microeconomic and macroeconomic overviews.
- It is a very cost-effective method of analyzing a company.
- Helps in planning new strategies.
Learning the benefits of Swot Analysis in detail will not only help identify professional strengths and weaknesses but also potential for professional development.
Limitations of SWOT Analysis
- It provides the company with limited information ( some external and internal factors can be missed).
- Only subjective solutions can be obtained. The person analyzing the SWOT table may need to be more objective.
- Does not provide a clear, actionable plan.
- There are no tools or methods to interpret the SWOT table accurately. The solutions may or may not be effective.
Instead of SWOT analysis, companies use other variations/alternatives of SWOT to perform business analysis more effectively. The four parts of SWOT analysis can’t guarantee that the company will be accurately rated.
See Also: Retail SWOT Analysis: Things to Know About the Retail Industry
FAQs
What are the four components of SWOT analysis?
The four steps of SWOT analysis are strength, weakness, opportunity, and threat.
What are the keys to a SWOT analysis?
To perform a proper SWOT analysis, ask what the four parts of SWOT analysis are. Then, figure out your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats by forming a table.
What are the 3 C's in SWOT analysis?
The 3 C's in a SWOT analysis are Competitors, Customers, and Corporation.
What are 4 examples of threats in SWOT analysis?
The 4 examples of threats are: Competition New Technology Environmental Factors Lack of capital
Conclusion
In this article, we can answer the question: what are the four components of SWOT analysis? Firstly, we examined the definitions and the use cases of strength, weakness, opportunity, and threat. Additionally, this analysis can help grow the business; every company needs it to sustain itself. Furthermore, SWOT analysis makes decision-making easier and smoothes the strategy planning process.