The retail life cycle is a crucial idea for companies in the retail sector. It has implications for marketing products and services and managing resources and staffing at different stages of the cycle. But why is it so important? This article will answer this question for you.
The Retail Life Cycle refers to the various stages a retail business goes through from its inception to its eventual decline or transformation. It consists of distinct phases that describe a retail business’s growth, maturity, and decay. Success in the cutthroat world of retail requires an understanding of the life cycle of a retail firm.
This article uncovers the details of the retail product life cycle and why it’s so important. Keep reading!
Check this out: Retail SWOT Analysis: Things to Know About the Retail Industry
What Is Retail Life Cycle?
Retailers have often faced the challenge of understanding the stages of the retail life cycle and how to utilize it best. The retail life cycle is an essential concept in business. It helps retailers develop strategies to maximize sales, optimize profits, and gain a competitive advantage. By understanding what stages a product or service goes through in its lifespan, retailers can ensure they take appropriate action to remain profitable and successful.
Retail life cycles are an essential part of the retail industry. They help businesses to plan for their future accurately. The cycle begins with product conception and ends with discontinuation or replacement. Knowing how to properly manage a product’s life cycle can be essential to staying competitive in the market. It will ensure that products remain profitable over time.
What Are The Phases Of The Cycle?
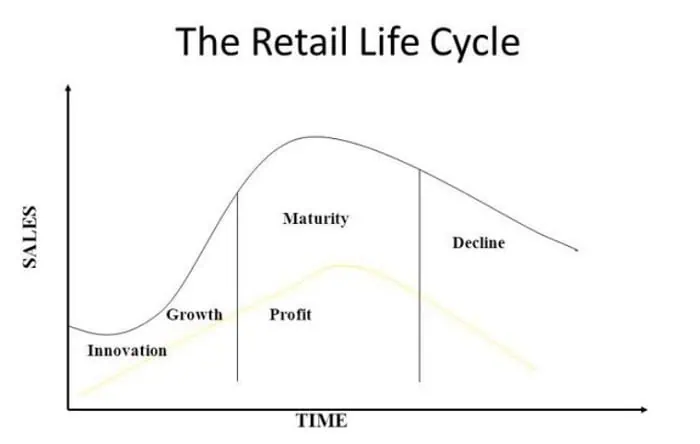
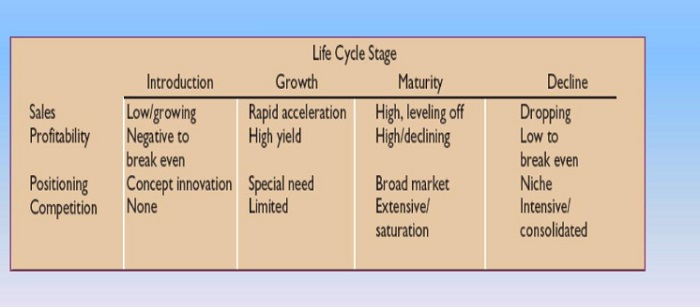
The retail life cycle consists of four distinct stages or phases: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline.
Introduction Phase
When new products are released into the market, the introduction stage begins. During this phase, retailers typically focus on generating consumer interest by investing in promotional activities such as advertising campaigns or special promotions.
Growth
When the product has gained some traction and started generating revenue, it moves into the growth stage, where its sales climb steadily. As demand rises during this period, profits start flowing in for retailers who can capitalize on it effectively.
Maturity
Retailers frequently concentrate on growing their market share when a product is mature. To do this, they must invest heavily in advertising campaigns and other promotional activities to maintain consumer interest. In this stage, the product is considered a ‘cash cow.’ It is likely to be the most profitable product in its portfolio.
Decline
Retailers must invest more resources into marketing efforts when product sales decline marketing efforts to maintain profitability. Sales of a product are likely to start slowing down and eventually stop in the decline stage.
In this stage, retailers can either discontinue the product or attempt to reposition it with a new branding strategy. A lack of demand for the product characterizes this stage. At this point, retailers are no longer interested in stocking the product, and, likely, most consumers are no longer interested in purchasing it.
Impact On Business Performance
Several factors can impact a business’s performance during the various stages of the retail life cycle. For example, companies experience a decline in profitability during the early stages of the process due to the cost of developing new products and launching marketing campaigns. However, the later phases of the process are much more profitable as the business has a better idea of how much consumers are willing to pay for its products and how to generate the highest profit margins.
In addition, businesses experience an increase in their sales during the later stages of the cycle as consumers continue to purchase their products believing there is a viable market for them. Businesses also experience a decrease in their operating expenses during the late stages of the cycle as they invest less in marketing costs to maximize profits. This enables them to make more profit without increasing prices to cover these costs.
Benefits Of Understanding the Cycle
By understanding the retail life cycle, businesses can develop strategies that will help them optimize their profits. Understanding a product’s life cycle is essential throughout the entire process, from manufacturing to sun-setting. Some of the benefits of understanding this process include:
1. Avoiding products that are unlikely to be successful in the marketplace.
This will help businesses save time and resources by eliminating products that are unlikely to be successful in the marketplace.
2. Identifying new products that are likely to be successful in the marketplace.
This help businesses identify potential new products that are likely to be successful in the marketplace.
3. Evaluating the market for existing products.
This will help businesses evaluate the market for existing products to determine if they are still viable products for their business.
4. Developing marketing strategies for products performing well in the marketplace.
This help businesses develop strategies for products already performing well in the marketplace to increase their market share and sales.
5. Developing a product launch strategy for products nearing the end of their life cycle.
This will help businesses develop a product launch strategy that will help extend the life of their existing products by introducing new and updated versions of these products to the market. A business that develops a successful marketing strategy for a particular product will typically see an increase in the demand for the product as more customers become aware of the product and begin to purchase the product regularly.
As demand increases, more suppliers will jump into the market to supply the product to meet the demand. As supply increases, prices will fall, and retailers will sell more product to meet this increased demand.
Challenges Of Implementing The Cycle
Once promoted products hit store shelves, managing inventory becomes a key challenge. This includes tracking stock levels, forecasting demand, and setting pricing strategies. Companies must also develop efficient supply chains to meet customer demands quickly.
As customers purchase items, businesses must track consumer behavior across different channels. By doing so, they can better forecast future trends and respond accordingly. Finally, retailers must focus on effective post-purchase services such as returns management. This is very important to meet customer satisfaction targets.
FAQS
What is an example of a good retail life cycle?
The life cycle of an Apple product is a good example. People wait in lines for hours to get their hands on the new iPhone, then use it for about a year, and then upgrade to the next one. The old ones are then put up for sale. Recycling companies then take the phones apart, extracting valuable metals and materials out of the phone to make new phones.
What are the factors affecting a retail life cycle?
There are many factors affecting a retail life cycle but a product's life cycle is the main one. The product life cycle is a graph of the sales of a new product over time. The graph is usually divided into four stages: growth, maturity, decline, and end of life. The product life cycle is very similar to the product lifecycle marketing mix.
Conclusion: Why Is It Important?
The retail life cycle is a key concept used in retail management to describe the stages of product development and sales within a retail business. Retailers must understand the different phases of a product’s lifecycle to maximize their business performance. Lifecycle Marketing and product lifecycle are closely related. The various phases that make up the retail cycle include introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. Each stage presents its own challenges and opportunities for retailers that can influence their overall business performance.
In the introduction phase, retailers must focus on building awareness of their products or services. They must develop effective marketing strategies to penetrate their target market and encourage customers to try out their offerings. Additionally, during this period, businesses should allocate significant resources toward research and development. By doing so, they can innovate new products or services based on customer feedback.